|
||
 |
||

Old
Nakamura 中村 house (Nagano)
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System. No reproduction or republication without written permission.
掲載のテキスト・写真・イラストなど、全てのコンテンツの無断複製・転載を禁じます。
|
||||||
| sarugashira 猿頭 | ||||||
| KEY WORD : architecture / general terms | ||||||
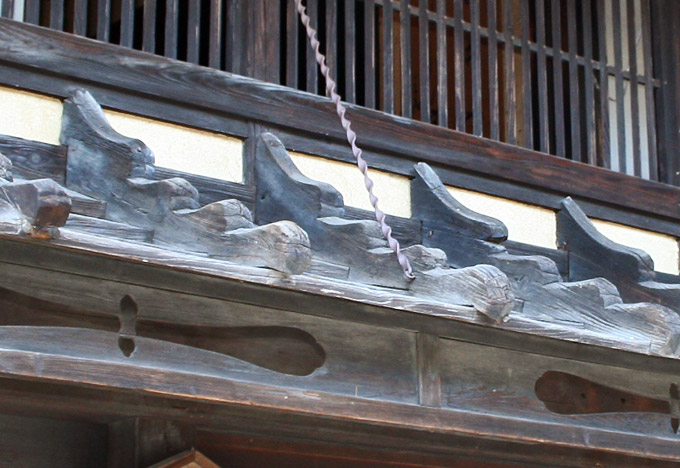
| Lit. monkey headpost. A general term for timber members of pentagonal cross-section, created by chamfering away the upper corners of a rectangle to create a triangular or pointed top which can shed water easily. It is used where long timber members may be exposed to the elements, for instance the rails of balustrades rankan 欄干, and in gates. The pointed side usually faces the elements. Much used, too, for the ridge pieces *munagi 棟木, and transverse bracing members of a type of used for roofed fences yanetsuki itabei 屋根付板塀, small roofs *koyane 小屋根, or sunshade pent roofs hiyokebisashi 日除け廂. The board roofs are made of from two, three or four overlapping strips of boarding, and the sarugashira, which are planted on top to hold the boarding in place, accordingly, have a stepped profile. When used for a roof with a varying pitch, the sarugashira pitch also changes. They are a feature of the street facades of urban vernacular residences *machiya 町家, at inn towns *shukubamachi 宿場町, especially in the Kiso 木曽 region of Nagano prefecture, where they form the top of a koyane usually associated with *hanedashi nikai はね出し二階. Slender iron chains extend from a position close to the top of the posts of the hanedashi nikai to the end of every 2nd or 3rd sarugashira, and from these the koyane is effectively suspended. The name may have derived from the visual effect of the slightly projecting ends of sarugashira used on pent or fence roofs, which may be said to resemble a row of monkeys' heads. | ||||||

Old
Nakamura 中村 house (Nagano)
|
||||||
| REFERENCES: | ||||||
| EXTERNAL LINKS: | ||||||
| NOTES: | ||||||
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System. No reproduction or republication without written permission. 掲載のテキスト・写真・イラストなど、全てのコンテンツの無断複製・転載を禁じます。 |
||||||