|
||
 |
||
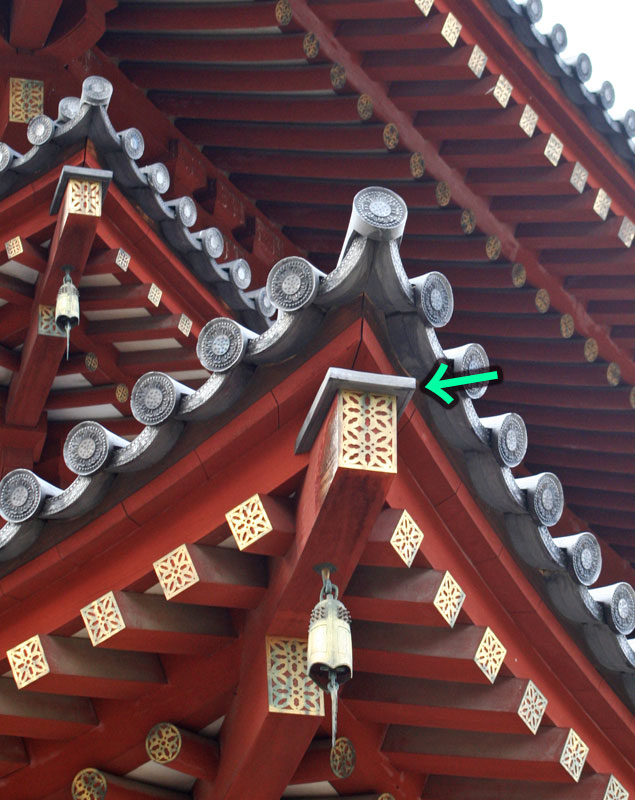

Yakushiji Kondou ςtΰ° (Nara)
@
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System.@No reproduction or republication without written permission.
fΪΜeLXgEΚ^ECXgΘΗASΔΜRecΜ³f‘»E]ΪπΦΆά·B
|
||||||
| @ | ||||||
| sumigi futagawara@χΨW’ | ||||||
| KEY WORD :@architecture / roofing tiles | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
| A long, narrow, rectangular tile cover used to protect the edge of a hip rafter from weathering. It is conjectured that these tiles were set into the angle made by the sides of the hip rafter and the tile roof surface to prevent rainwater from seeping under the roof tiles. The tail end of the protective cover usually has a right angle cut to fit over the eave support *kayoi . The upper edge is made high on one such tile unearthed at the site of Naniwa-no-Miya οg{, Osaka, to let rainwater run off easily. One found at Yakushiji ςt in Nara is decorated with *renjumon AμΆ, a bead motif at the top and bottom. It has a flower-like cloud pattern ka'unmon Τ_Ά on the surface in between the boards. The tile is short and has a lip *tamabuchi Κ at the tail end, indicating that it was joined to another tile of the same type. Another example from the Heian period unearthed at Rokuharamitsuji Zg § in Kyoto, is decorated with thunderbolt pattern and ritual implements used in the esoteric Shingon ^Ύand Tendai Vδ sects. It was found along with an eave-end tile *nokimarugawara ¬Ϋ’, with a circular pendant *gatou ’, attached and ornamented with a Sanskrit character *bonjimon Ά. | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
 Yakushiji Kondou ςtΰ° (Nara)
|
||||||
@ |
||||||
| REFERENCES: | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
| EXTERNAL LINKS: | ||||||
| @@ | ||||||
| NOTES: | ||||||
| @ | ||||||
(C)2001 Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System.@No reproduction or republication without written permission. fΪΜeLXgEΚ^ECXgΘΗASΔΜRecΜ³f‘»E]ΪπΦΆά·B |
||||||
| @ |